Server Cluster
Introduction
Netris Server Cluster makes it possible to define network boundaries by referencing a list of compute or storage nodes (Netris Server objects).
Behind the scenes, Netris figures out which VXLANs, VLANs, Pkeys, and NVLink partitions, when appropriate to configure for every appropriate switch and switch port. The Server Cluster object will also create the underlying V-Net, VPC, and other Netris objects.
This helps infrastructure operators create, edit, and delete network boundaries by focusing only on the list of servers and not worrying about switch ports, GUIDs, GPU UIDs,or any other implementation details.
Server Cluster Template
A Server Cluster Template is a JSON array of V-Nets to create, their types, and server NICs to be assigned to these V-Nets. The template must be defined before a Server Cluster can be created.
In a Server Cluster Template you define:
What V-Nets to create and their types (VXLAN, VLAN, UFM, NVLink, and others)
What subnets to assign to each these V-Nets, when applicable
Which server NICs map to these V-Nets
Other applicable settings specific to Ethernet, InfiniBand, and NVLink fabrics
You can find more information about these primitives in the V-Net and IP Address Management Netris documentation.
Based on a Server Cluster Template, Netris will:
Create VPCs, V-Nets, and IP allocations and subnets
Look up and configure the correct switch ports (front-end, back-end, management)
Apply VXLANs, VLANs, LAGs, InfiniBand PKeys, NVLink partitions, and other network configurations
Here are several template examples followed by detailed descriptions of every field.
Warning
For l3vpn type to function properly, the /31 links’ addresses must be prepopulated. This is best done with Terraform during the server onboarding phase. See Netris Terraform Provider for details.
Server Cluster Template Examples:
Ethernet-only Fabric Example
This example is common for AI fabrics where both Frontned (North-South) and Backend (East-West) networks are based on Ethernet. A Server Cluster referenced to this template will create two L2VPN VXLAN V-Nets and one L3VPN VXLAN V-Net. V-Net names will start with the name of the server cluster and end with the value of each postfix attribute.
[
{
"postfix": "E-W",
"type": "l3vpn",
"vlan": "untagged",
"vlanID": "auto",
"serverNics": [
"eth3",
"eth4"
]
},
{
"postfix": "N-S",
"type": "l2vpn",
"vlan": "untagged",
"vlanID": "auto",
"serverNics": [
"eth1",
"eth2"
],
"ipv4Gateway": "192.168.10.254/24",
"ipv4DhcpEnabled": true
},
{
"postfix": "mgmt",
"type": "l2vpn",
"vlan": "untagged",
"vlanID": "auto",
"serverNics": [
"eth0"
],
"ipv4Gateway": {
"assignType": "auto",
"allocation": "10.10.0.0/16",
"childSubnetPrefixLength": 24,
"hostnum": 1
}
}
]
Infiniband Fabric Example
This example is common for AI fabrics where the frontend is based on Ethernet and the backend is based on InfiniBand. A Server Cluster referencing this template will create two L2VPN type VXLAN V-Nets and will automatically configure the Ethernet switches, and will configure one PKey with appropriate GUIDs in the NVIDIA UFM (Infiniband controller).
[
{
"postfix": "E-W",
"type": "netris-ufm",
"ufm": "ufm-88",
"pkey": "auto"
},
{
"postfix": "N-S",
"type": "l2vpn",
"vlan": "untagged",
"vlanID": "auto",
"serverNics": [
"eth9",
"eth10"
],
"ipv4Gateway": "10.0.0.1/24",
"ipv4DhcpEnabled": true
},
{
"postfix": "mgmt",
"type": "l2vpn",
"vlan": "untagged",
"vlanID": "auto",
"serverNics": [
"eth11"
],
"ipv4Gateway": "192.168.100.1/24",
"ipv4DhcpEnabled": true
}
]
You can find more details about NVIDIA UFM (InfiniBand) integration in Netris UFM documentation.
NVLink (NVL72 or NVL144) Fabric Example
In systems where NVLink Multi-Node fabric is present, Netris can be configured to automatically create GPU partitions within the appropriate NVL72 or NVL144 NVLink domain.
[
{
"postfix": "E-W",
"type": "netris-ufm",
"ufm": "ufm-88",
"pkey": "auto"
},
{
"postfix": "NVL",
"type": "netris-nvlink",
"partition": "auto"
},
{
"postfix": "N-S",
"type": "l2vpn",
"vlan": "untagged",
"vlanID": "auto",
"serverNics": [
"eth9",
"eth10"
],
"ipv4Gateway": "10.0.0.1/24",
"ipv4DhcpEnabled": true
},
{
"postfix": "mgmt",
"type": "l2vpn",
"vlan": "untagged",
"vlanID": "auto",
"serverNics": [
"eth11"
],
"ipv4Gateway": "192.168.100.1/24",
"ipv4DhcpEnabled": true
}
]
You can find more detail about the NVIDIA NMX-C (NVLink Multi-Node / NVL72 / NVL144) integration in NMX-C (NVLink) Integration Plugin for Netris Controller.
IPv6 Example
IPv6 is fully supported in Netris. This example showcases how to optionally enable IPv6 on any V-Net segment of the Server Cluster Template.
[
{
"postfix": "E-W",
"serverNics": [
"eth1",
"eth2",
"eth3",
"eth4",
"eth5",
"eth6",
"eth7",
"eth8"
],
"type": "l3vpn",
"vlan": "untagged",
"vlanID": "auto"
},
{
"postfix": "N-S",
"serverNics": [
"eth9",
"eth10"
],
"type": "l2vpn",
"vlan": "untagged",
"vlanID": "auto",
"ipv6Gateway": "2001:db8:1::1/64"
},
{
"postfix": "OOB-MGMT",
"serverNics": [
"eth11"
],
"type": "l2vpn",
"vlan": "untagged",
"vlanID": "auto",
"ipv6Gateway": {
"assignType": "auto",
"allocation": "2001:DB8::/32",
"childSubnetPrefixLength": 64,
"hostnum": 1
}
}
]
Template Fields Explained:
Each object in the Vnets JSON array may include a combination of the following key-value pairs
postfix: A string appended to the server cluster name to form the V-Net name.
type: A string specifying the type of V-Net (l2vpn, l3vpn, netris-ufm, netris-nvlink).
vlan: A string specifying whether the V-Net is tagged or untagged. Only untagged is permitted at this time.
vlanID: A string specifying the VLAN ID. Only auto is permitted at this time.
serverNics: An array of Netris server NIC names on the server that will be associated with this V-Net.
ipv4Gateway: When type:l2vpn one of the following values:
A string specifying the IPv4 gateway for V-Net in CIDR notation
A string specify to force the operator to enter the gateway explicitly at cluster creation
an object (see Advanced Uses) with the following properties:
assignType: A string indicating the type of assignment. Only auto is permitted at this time.
allocation: A string specifying the IPv4 address allocation, a supernet from which the child subnets will be derived.
childSubnetPrefixLength: An integer specifying the prefix length for child subnets.
hostnum: An integer specifying the host number for the gateway.
ipv4DhcpEnabled: A boolean to enable/disable DHCP for IPv4.
ipv6Gateway: When type:l2vpn one of the following values:
A string specifying the IPv6 gateway for V-Net in CIDR notation
A string specify to force the operator to enter the gateway explicitly at cluster creation
an object (see Advanced Uses) with the following properties:
assignType: A string indicating the type of assignment. Only auto is permitted at this time.
allocation: A string specifying the IPv6 address allocation, a supernet from which the child subnets will be derived.
childSubnetPrefixLength: An integer specifying the prefix length for child subnets.
hostnum: An integer specifying the host number for the gateway.
Ufm: Nvidia UFM controller identifier (ufm_id) for V-Net type:netris-ufm. See Netris UFM documentation for details.
Pkey: Pkey settings when V-Net type:netris-ufm. Only auto is permitted at this time.
partition: NVLink partition settings when V-Net type:netris-nvlink. Only auto is permitted at this time.
Field |
type: l2vpn |
type: l3vpn |
type: netris-ufm |
type: netris-nvlink |
|---|---|---|---|---|
postfix |
✅ required |
✅ required |
✅ required |
✅ required |
type |
✅ required |
✅ required |
✅ required |
✅ required |
vlan |
✅ (must be “untagged”) |
✅ (must be “untagged”) |
❌ |
❌ |
vlanID |
✅ (auto only) |
✅ (auto only) |
❌ |
❌ |
serverNics |
✅ required |
✅ required |
❌ |
❌ |
ipv4Gateway |
optional |
❌ |
❌ |
❌ |
ipv4DhcpEnabled |
optional (requires ipv4Gateway) |
❌ |
❌ |
❌ |
ipv6Gateway |
optional |
❌ |
❌ |
❌ |
ufm |
❌ |
❌ |
✅ (auto only) |
❌ |
pkey |
❌ |
❌ |
❌ |
✅ (auto only) |
Adding a Server Cluster Template
To define a Server Cluster Template in the web console, navigate to Services->Server Cluster Template, click +Add, give the template a descriptive name like ‘GPU-Cluster-Template’. Enter V-Nets, their configuration parameters, and which server NICs must be placed into these V-Nets as a JSON array.

Advanced Uses
Non-overlapping subnets
Netris fully supports overlapping IP addresses across VPCs, but some use cases such as shared storage access or external network integrations, may require globally unique subnets for the north-south (frontend) fabric. In these cases, you can configure Netris to automatically allocate non-overlapping subnets from a larger pool, ensuring compatibility with such constraints.
This is done by specifying the allocation key in the ipv4Gateway or ipv6Gateway object and providing a supernet from which child subnets will be derived. This approach ensures that the IP addresses assigned to each V-Net do not overlap.
[
{
"postfix": "E-W",
"type": "l2vpn",
"vlan": "untagged",
"vlanID": "auto",
"serverNics": [
"eth7",
"eth8"
],
"ipv6Gateway": {
"assignType": "auto",
"allocation": "2001:DB8::/32",
"childSubnetPrefixLength": 64,
"hostnum": 1
}
},
{
"postfix": "N-S",
"type": "l2vpn",
"vlan": "untagged",
"vlanID": "auto",
"serverNics": [
"eth9",
"eth10"
],
"ipv4Gateway": {
"assignType": "auto",
"allocation": "10.0.0.0/16",
"childSubnetPrefixLength": 24,
"hostnum": 1
},
"ipv4DhcpEnabled": true
},
{
"postfix": "OOB",
"type": "l2vpn",
"vlan": "untagged",
"vlanID": "auto",
"serverNics": [
"eth11"
],
"ipv4Gateway": "192.168.0.254/24",
"ipv4DhcpEnabled": true
}
]
Specify gateway
In case you want to specify the IP gateway manually when creating a Server Cluster object, you can indicate this in the Server Cluster Template by setting the ipv4Gateway (or ipv6Gateway) key to specify . Netris will prompt for the exact gateway address at the time of defining the cluster and will infer the subnet address to be assigned to the V-Net.
[
{
"postfix": "UFM8-E-W",
"type": "netris-ufm",
"ufm": "ufm-88",
"pkey": "auto"
},
{
"postfix": "N-S",
"type": "l2vpn",
"vlan": "untagged",
"vlanID": "auto",
"serverNics": [
"eth9",
"eth10"
],
"ipv4Gateway": "specify",
"ipv6Gateway": "specify"
},
{
"postfix": "OOB-MGMT",
"type": "l2vpn",
"vlan": "untagged",
"vlanID": "auto",
"serverNics": [
"eth11"
],
"ipv4Gateway": "specify",
"ipv6Gateway": "specify"
}
]
Creating Server Cluster
With templates defined, you can create Server Clusters by referencing these templates and specifying a list of servers. This operation triggers the creation of the applicable network primitives such as V-Nets, IP subnets, Pkeys and other InfiniBand primitives based on the template’s definitions.
Adding a Server Cluster
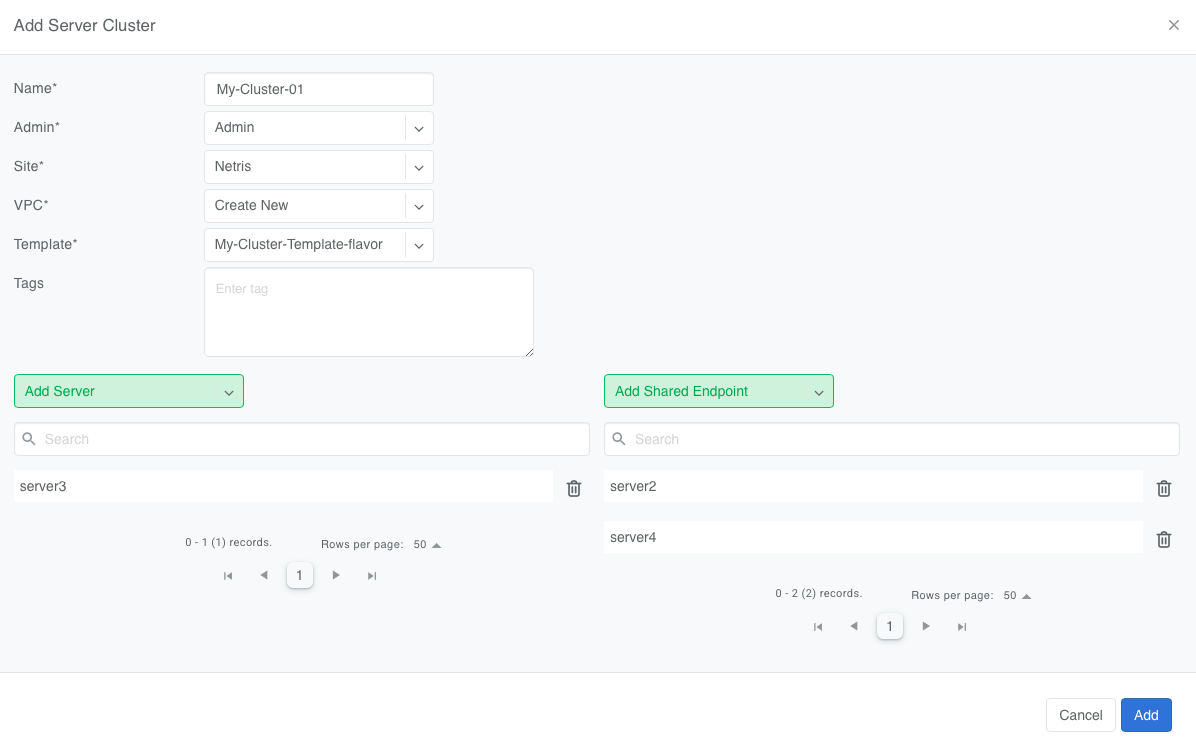
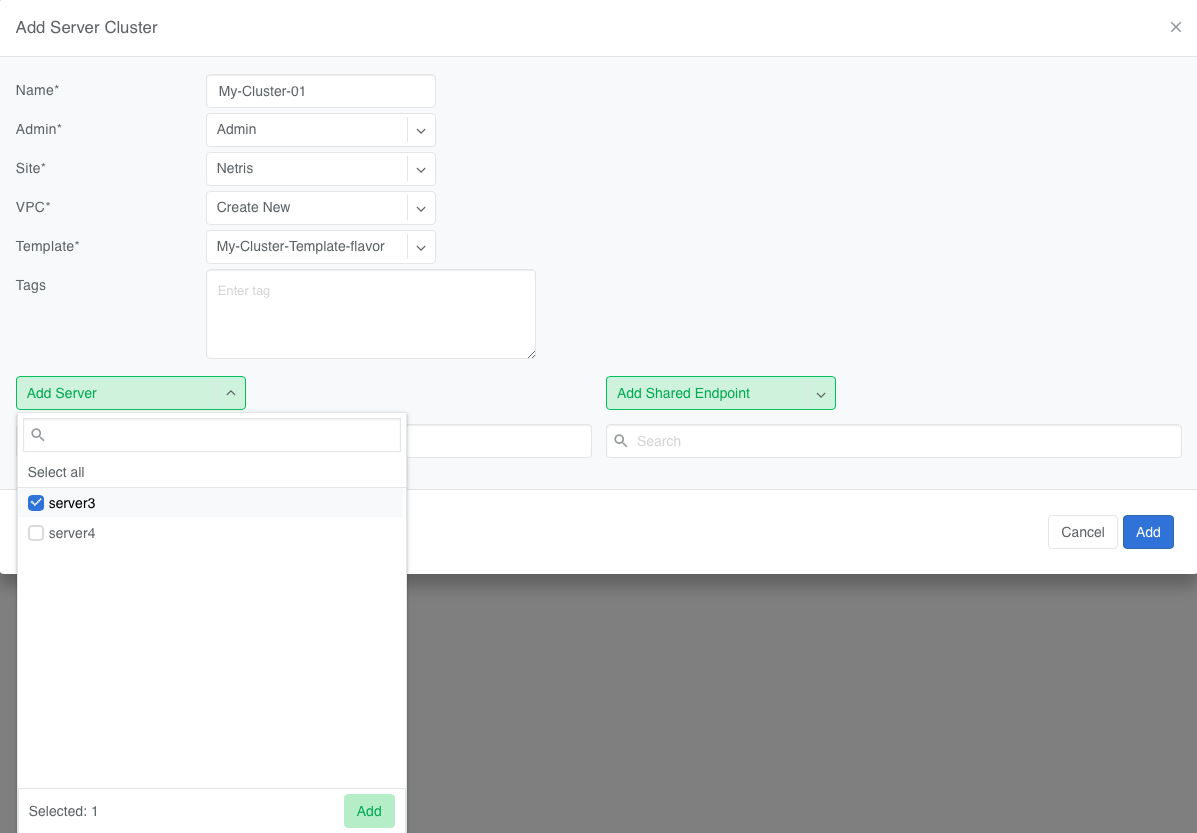
To define a Server Cluste, navigate to Services->Server Cluster and click +Add. Give the new cluster a name, set Admin to the appropriate owner (this defines who can edit/delete this cluster and only servers already assigned to this owner will be available for selection), set the site, set VPC to “Create New”, select the Template created earlier, and click +Add Server or +Add Shared Server to start selecting server members. Click Add.
When you click the blue Add button, Netris will create the VPC, V-Nets, and IP subnets as defined in the template. It will also configure the switch ports for each server based on the NIC names specified in the template.
Note
A VPC will be created automatically when “Create New” is selected.
After creation, the template, the VPC, and the site fields are locked.
The same Netris NIC name must be used consistently across all server objects in a cluster. For example, when eth10 is assigned to a V-Net in the template, Netris will assign every switch port that corresponds to every server’s eth10 to the same V-Net throughout the server cluster.
Server Cluster Fields Explained:
Name: A descriptive name for the server cluster.
Admin: The administrative owner of this server cluster.
Site: The site where the server cluster is located.
VPC: The VPC to which the server cluster belongs. Typically set to “Create New” to generate a new VPC.
Template: The Server Cluster Template that defines the Netris primitives for this cluster.
Servers: A list of servers that are dedicated members of this cluster.
SharedEndpoints: A list of servers that are members of this cluster, but can also be added to other clusters.