NVIDIA NMX-C (NVLink) Integration Plugin for Netris Controller
Overview
The Netris-NMX plugin provides seamless integration between Netris Controller and NVIDIA NMX-C (NMX-Controller) for AI infrastructures with NVIDIA NVLink Multi-Node (NVL72/NVL144) fabrics present. This integration allows infrastructure operators to define compute multi-tenancy in a single place through Netris, significantly simplifying management across all network types.
Key Benefits
Unified Management Interface: Define tenant isolation by simply listing servers in a Server Cluster object
Automated Provisioning: Automatically configure NVLink partitions on NVL72/NVL144 Multi-Node fabrics to align with tenant boundaries configured on other fabrics such as East-West (via Ethernet or InfiniBand) and North-South Ethernet.
Simplified Operations: Eliminate the need to manage SwitchPorts, VLANs, VRFs on Ethernet, GUIDs, PKeys, SHARP groups on InfiniBand), and NVLink partitions and GPU UIDs separately.
Architecture
The Netris-NMX plugin acts as the integration layer between Netris Controller and NVIDIA NMX-Controller:
Netris Controller: Orchestrates the Ethernet switches and provides the primary user interface.
NVIDIA NMX-C: Manages the NVLink Multi-Node fabric switches and provides specialized NVLink functionality.
Netris-NMX Plugin: Synchronizes configurations between both systems
Tip
NVIDIA NetQ (NMX-M) is not required by Netris, but it is recommended for granular Network + GPU telemetry
When you define a Server Cluster in Netris, the plugin automatically:
Discovers GPU UIDs for each server using the preloaded GPU ledger.
Creates and manages appropriate NVL partitions in NMX-C
Assigns appropriate GPU UIDs to appropriate NVL partitions
The Netris-NMX plug agent runs continuously and validates that the operator’s intent is correctly applied every 20 seconds by default. If the NVLink partition doesn’t match the intent declared in the Netris Controller, the Netris-NMX agent will enforce the intent in the NMX-Controller.
The NMX-Controller remains the source of truth for the state of the GPU assignments to NVLink partitions. The Netris Controller is the source of truth for the operator’s intent, and the Netris agent will continuously enforce the operator’s intent as expressed through the Server Cluster object in the Netris Controller.
When more than one NMX-Controller is defined in the configuration, Netris will automatically discover which NMX-Controller creates the NVLink partition and will only create the partitions in the appropriate NMX-Controllers.
High-Level Workflow
Preload GPU mapping
Configure NVLink agent
Agent discovers the current state from NMX-C(s)
Netris determines the desired partition based on the server cluster template and server cluster membership.
Agent reconciles every 20s
Debug via script
Tip
Server Cluster is the only supported way for Netris to manage NVLink partitions.
Tip
Netris does not perform any additional NVLink management tasks, like NVLink switch life cycle management, etc., other than creating, modifying, and destroying NVLink partitions and adding or removing GPU UIDs to those partitions. NVIDIA NMX-C is the NVLink fabric manager.
Prerequisites
Before installing the Netris-NMX plugin, ensure:
A functioning Netris Controller environment
A properly configured NVIDIA NMX-C installation
Network connectivity between the Netris Controller or a dedicated server running the Netris-NMX plugin and the NVIDIA NMX-Controller.
Appropriate access credentials for both platforms
Installation
Installing the plugin
The Netris-NMX plugin can be installed on the same server as the Netris Controller or on a dedicated server, depending on customer requirements and network topology.
If a dedicated server option is chosen, ensure that the server running the Netris-NMX plug can reach all the NVIDIA NMX-Controllers in the environment. This dedicated server must also be able to reach the Netris Controller. All communication between the Netris Controller, NVIDIA NMX-C, and the Netris-NMX plug is initiated from the server running the Netris-NMX plugin.
Download the Kubernetes deployment YAML file:
wget https://get.netris.io/netris-controller-nmx.yaml
Edit the YAML file to update the secret values based on your environment:
nmx-config:
verify-ssl: true
cert-file: /home/ubuntu/netris-nvlink-agent/client.crt
key-file: /home/ubuntu/netris-nvlink-agent/client.key
root-ca: /home/ubuntu/netris-nvlink-agent/rootCA.crt
common-name: nmxc-01.acme.com
nmx-c:
nmxc_01:
addresses:
- nmxc-01.acme.com:8601
Apply the configuration to your Kubernetes cluster:
kubectl apply -f netris-controller-nmx.yaml
Loading GPU inventory
Netris must have the mapping between the GPU UIDs and the servers those GPUs are installed in preloaded before automatic NVL partition management can start.
Here is an example of the GPU UID inventory file:
hgx-pod00-su0-h00,875835130816197840
hgx-pod00-su0-h00,961186615343340613
hgx-pod00-su0-h00,796824814706104730
hgx-pod00-su0-h00,684212070855729123
hgx-pod00-su0-h01,718625720642846212
hgx-pod00-su0-h01,788578661925003442
hgx-pod00-su0-h01,910329703472956766
hgx-pod00-su0-h01,814561743235261831
hgx-pod00-su0-h02,996615732638596030
hgx-pod00-su0-h02,884228998345288014
hgx-pod00-su0-h02,730725932032980822
hgx-pod00-su0-h02,749618463645136824
hgx-pod00-su0-h03,893225768947662203
hgx-pod00-su0-h03,825286183620844317
hgx-pod00-su0-h03,784007583961668668
hgx-pod00-su0-h03,713366763878128965
…
Execute netris-nvl-loader script to import the GPU UID inventory into the Netris Controller
./netris-nv-loader --csv-file gpu-mapping.csv --netris-url "https://conroller.acme.com" --username "admin" --password "passw0rd"
Where
--csv-file <filename> specifies the comma-separated value (CSV) file with GPU UID inventory
--netris-url "<URL>” specifies the Netris Controller URL
--username "<username>" specifies the Netris administrator username
--password "<password>" specifies the Netris administrator password
Upon successful import, you should see output similar to the one below
INFO [0000] Found 72 GPU mappings in CSV file
INFO [0000] Logging in to Netris…
INFO [0000] Successfully logged in to Netris
INFO [0000] Fetching inventory from Netris (import mode)...
INFO [0001] Found 38 server inventory items
INFO [0002] Successfully updated server ‘hgx-pod00-su0-h00’ with 4 GPU mappings
INFO [0003] Successfully updated server ‘hgx-pod00-su0-h01’ with 4 GPU mappings
INFO [0004] Successfully updated server ‘hgx-pod00-su0-h02’ with 4 GPU mappings
…
You can further confirm successful import by examining the appropriate server objects in the Netris controller. In the Custom JSON field of each GPU server in scope, you should see a JSON object similar to the following
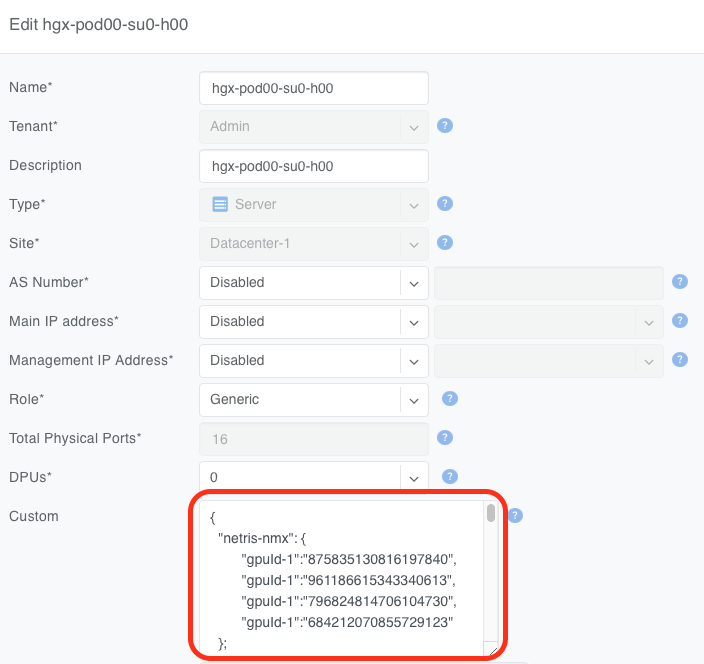
Warning
Netris does not enforce the completeness of the GPU inventory or whether the mapping is correct. Please ensure that you validate your inventory file content before loading the inventory into the Netris Controller.
Tip
In the most basic sense, when you create a Server Cluster using a Server Cluster Template that references NVLink integration, as shown in the Server Cluster documentation, Netris will look up GPU UIDs in the Netris server inventory for each server in the Server Cluster and create one NVLink partition per NMX-C named after the Server Cluster, including the Server Cluster ID, and assign the appropriate GPUs to that partition.
Warning
NVIDIA does not support NVLink partitions spanning more than one NVL domain.
Netris-NMX Plugin Configuration Parameters
The following configuration options are available in the Netris-NMX plugin YAML configuration file:
nmx-config - top-level mapping for the plugin configuration
verify-ssl - key to signal the plug whether to use TLS authentication when accessing the NMX-Controller
cert-file - absolute path to the client certificate
key-file - absolute path to the private key of the client certificate
root-ca - absolute path to the root CA certificate file.
common-name - must match the value of the CN field of the certificate presented by the NMX-Controller.
nmx-c - contains a mapping describing each NMX-Controller you’d like Netris to create NVLink partitions in. It must contain at least one key with a value of a list of hostnames and port numbers
addresses - is a list of hostnames and port numbers of each NMX-C node in an NMX-C HA cluster.
Each NMX-C must be presented through a separate key. The addresses key is intended to contain a list of every node in a single NMX-C HA instance.
In the deployment where each NMX-Controller requires a separate client authentication certificate, the relevant keys may be included in the mapping for that specific NMX-Controller, like so:
nmx-config:
verify-ssl: true
cert-file: /home/ubuntu/netris-nvlink-agent/client.crt
key-file: /home/ubuntu/netris-nvlink-agent/client.key
root-ca: /home/ubuntu/netris-nvlink-agent/rootCA.crt
common-name: nmxc-x.acme.com
nmx-c:
nmxc_01:
cert-file: /home/ubuntu/netris-nvlink-agent/client01.crt
key-file: /home/ubuntu/netris-nvlink-agent/client01.key
root-ca: /home/ubuntu/netris-nvlink-agent/rootCA.crt
common-name: nmxc-01.acme.com
addresses:
- nmxc-01.acme.com:8601
nmxc_02:
addresses:
- nmxc-02.acme.com:8601
nmxc_03:
addresses:
- nmxc-03.acme.com:8681
- nmxc-03.acme.com:8682
After successfully installing and configuring the Netris-NMX agent, you can use Server Cluster to create NVLink partitions via the creation of Server Clusters. You must update your Server Cluster Template to include NVLink integration. See the Server Cluster documentation for more details.
Verification
Netris ships nmx-get-partititions.sh script, which helps the operator to verify proper operation of the Netris-NMX plugin.
Below are a few examples of running the verification script.
The output shows that only a default partition is present in the NMX-Controller and no GPU UIDs are assigned to it.
> ./nmx-get-partitions.sh
=== NMX-C Partition Information ===
Gateway ID: gateway_id
Host: nmxc-01.acme.com:8601
===================================
Partition ID: 32766
Name: Default Partition
Number of GPUs: N/A
GPU UIDS:
- None
Health: NAX_PARTITION_HEALTH_HEALTHY
Type: NMX_PARTITION_TYPE_GPUUID_BASED
The customer may choose to configure the NVLink domain with a default partition (see NVIDIA NVLink Multi-Node Documentation for more details). Netris is fully compatible with this scenario and will remove the GPU UIDs from the default NVLink partition when those GPU UIDs are scheduled to be assigned to a new tenant partition.
The output below shows a new NVLink partition created with 8 GPUs after a server cluster was instantiated containing servers with those GPU UIDs. Note that the partition name contains the Server Cluster ID (192 in this example), which may be helpful during troubleshooting. Netris will always include the Server Cluster ID in the NVLink partition name.
> ./nmx-get-partitions.sh
=== NMX-C Partition Information ===
Gateway ID: gateway_id
Host: nmxc-01.acme.com:8601
===================================
Partition ID: 32766
Name: Default Partition
Number of GPUs: N/A
GPU UIDS:
- None
Health: NMX_PARTITION HEALTH_ HEALTHY
Туре: NMX_PARTITION_TYPE_GPUUID_BASED
—-----------------------------------
Partition 1D: 8593
Name: netris-cluster-192
Number of GPUs: 8
GPU UIDs:
- 875835130816197840
- 961186615343340613
- 796824814706184730
- 684212070855729123
- 718625720642846212
- 788578661925003442
- 910329783472956766
- 814561743235261831
Health: NMX_PARTITION HEALTH_ HEALTHY
Type: N/A
—-----------------------------------
Maintenance and Deprovisioning
If you need to perform maintenance on one or more GPU servers that are part of an NVLink partition, Netris recommends that you remove those servers from the Server Cluster before performing this maintenance. Doing so will remove the relevant GPU UIDs from the tenant’s NVLink partition.
Warning
Removing a server from a Server Cluster will also remove this server from ever and all V-Nets and VPCs that this server was a member of as a result of being a member of a Server Cluster. Netris will not remove this server from any V-Nets where the switch ports connected to this server were assigned to this V-Net manually or using Labels.
